Explore interesting arduino based projects and tutorials based on different types of arduino baords like Arduino Uno, Arduino Pro Mini, etc. These simple arduino projects are explained well and you can find the complete guide to DIY these projects with the help of circuit diagrams, source codes and videos. Sketch uses 17524 bytes (54%) of program storage space. Maximum is 32256 bytes. Global variables use 832 bytes (40%) of dynamic memory, leaving 1216 bytes for local variables. Maximum is 2048 bytes. Arduino-uno esp8266. Improve this question. Edited Jul 10 '19 at 10:10. Fuzzy logic projects,fuzzy logic projects using matlab,fuzzy logic project ideas,fuzzy logic project report,fuzzy logic project list,fuzzy logic projects source code, 2019 Fuzzy logic projects,2018 Fuzzy logic projects,ieee Fuzzy logic projects,Fuzzy logic project basepaper,Fuzzy logic project pdf.
You can generate code for evaluating a fuzzy inference system using MATLAB® Coder™. For more information on generating code, see Code Generation (MATLAB Coder).
To generate code for evaluating fuzzy systems, you must first create a fuzzy inference system (FIS). For more information, see Build Fuzzy Systems at the Command Line and Build Fuzzy Systems Using Fuzzy Logic Designer.
While this example generates code for a type-1 Mamdani fuzzy inference system, the workflow also applies to Sugeno and type-2 fuzzy systems.
Generating code using MATLAB Coder does not support fuzzy FIS objects (mamfis, sugfis, mamfistype2, sugfistype2). To generate code for evaluating fuzzy systems, you must convert your fuzzy inference system objects into homogeneous structures using the getFISCodeGenerationData function.
Embed FIS Data in Generated Code
You can embed the data for your fuzzy inference system within the generated code. Use this option if you do not want to change the FIS data after compilation.
First, create a fuzzy system, or load a fuzzy system from a .fis file. For this example, load the fuzzy system from tipper.fis.
To use this FIS for code generation, convert it to a homogeneous structure.
By default, getFISCodeGenerationData assumes that the FIS object is a type-1 system. To generate code for a type-2 system, you must indicate the system type using getFISCodeGenerationData(fisObject,'type2').
Create a function for evaluating the fuzzy system fis for a given input vector x. Within this function, you can specify options for the evalfis function using evalfisOptions.
Generate code for evaluatefis1, specifying that the fis input argument is constant. You can specify different targets for your build, such as a static library, an executable, or a MEX file. For this example, generate a MEX file.
To verify the execution of the MEX file:
Evaluate the MEX file for one or more input values. When you call the MEX file, specify the same FIS structure that you used at compile time.
Evaluate the original FIS for the same input values using
evalfis. When evaluating usingevalfis, use the same homogeneous FIS structure.Compare the evaluation results.
The MEX file output matches the evalfis output.
Alternatively, you can embed the FIS data in the generated code by reading the FIS data from a file at code generation time. Specify a function for evaluating a fuzzy system for given input vector x. Within this function, read the FIS data from the file tipper.fis.
Generate code for evaluatefis2.
Verify the execution of the MEX file using the same input values for x. In this case, you do not have to specify the original FIS structure used at compile time.
Generate Code for Loading FIS Data at Run Time
You can generate code for evaluating a FIS that is read from a .fis file specified at run time. In this case, the FIS data is not embedded in the generated code. Specify a function for evaluating the fuzzy system defined in the specified file fileName for a given input vector x.
Define input data types for this function.
Generate code for evaluatefis3.
Fuzzy Logic Cooker
Verify the execution of the MEX file using the same input values for x. In this case, you specify the name of the .fis file.
Each time you run evaluatefis3, it reloads the fuzzy system from the file. For computational efficiency, you can create a function that only loads the FIS when a new file name is specified.
Generate code evaluatefis4. The input data types for this function are the same as for evaluatefis3.
Verify the execution of the MEX file using the same input values file name.
Generate Code for Single-Precision Data
The preceding examples generated code for double-precision data. To generate code for single-precision data, specify the data type of the input values as single. For example, generate code for evaluatefis2 using single-precision data.
Verify the MEX file execution, passing in single-precision input values.
See Also
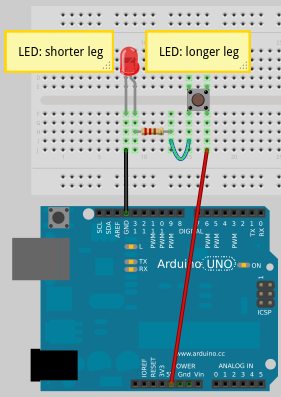
Source Code Fuzzy Logic Arduino Code
evalfis | getFISCodeGenerationData